Running Jobs¶
To run an application (job) , computational resources must be allocated. ARIS uses SLURM Workload Manager (Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management) to distribute workloads across the supercomputer. For more information check the slurm quick start guide. https://computing.llnl.gov/linux/slurm/quickstart.html
Slurm has three key functions.
First, it allocates exclusive and/or non-exclusive access to resources (compute nodes) to users for some duration of time so they can perform work.
Second, it provides a framework for starting, executing, and monitoring work (normally a parallel job) on the set of allocated nodes.
Finally, it arbitrates contention for resources by managing a queue of pending work.
Common terms:
nodes: the compute resource in SLURMpartitions(queues): node groupsjobs: allocations of resourcesjob steps: sets of tasks within a job.
Resource Queues¶
In order to use all the nodes efficiently and in a fair share fashion, resources are distributed in queues (partitions). Queues group nodes into logical sets, each of which has an assortment of constraints such as job size limit, job time limit, users permitted to use it, etc.
To determine what partitions exist on the system, what nodes they include, and general system state.
use the sinfo command.
sinfo -s
ARIS queue (partition) overview:
Queue Table¶
| PARTITION | DESCRIPTION | AVAIL | TIMELIMIT | NODES | NODELIST |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| compute | Compute nodes w/o accelerator | up | 2-00:00:00 | 426 | node[001-426] |
| fat | Fat compute nodes | up | 2-00:00:00 | 24 | fat[01-24] |
| taskp | Serial jobs queue | up | 2-00:00:00 | 20 | fat[25-44] |
| gpu | GPU accelerated nodes | up | 2-00:00:00 | 44 | gpu[01-44] |
| phi | MIC accelerated nodes | up | 2-00:00:00 | 18 | phi[01-18] |
- compute queue: Is intended to run parallel jobs on the THIN compute nodes.
- fat queue: Is dedicated to run parallel jobs on the FAT compute nodes.
- taskp queue: Is intended to run multiple serial jobs on the FAT compute nodes.
- gpu queue: Provides access on the GPU accelerated nodes.
- phi queue: Provides access on the PHI accelerated nodes.
The scontrol command can be used to report more detailed information partitions and configuration
:$ scontrol show partition PartitionName=compute AllowGroups=ALL AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL AllocNodes=ALL Default=YES DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=UNLIMITED MinNodes=1 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED Nodes=node[001-426] Priority=1 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO Shared=NO PreemptMode=OFF State=UP TotalCPUs=8520 TotalNodes=426 SelectTypeParameters=N/A DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=57344 PartitionName=fat AllowGroups=ALL AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL AllocNodes=ALL Default=NO DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=UNLIMITED MinNodes=1 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED Nodes=fat[01-24] Priority=1 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO Shared=NO PreemptMode=OFF State=UP TotalCPUs=960 TotalNodes=24 SelectTypeParameters=N/A DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=507904 PartitionName=taskp AllowGroups=ALL AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL AllocNodes=ALL Default=NO DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=UNLIMITED MinNodes=1 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED Nodes=fat[25-44] Priority=1 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO Shared=NO PreemptMode=OFF State=UP TotalCPUs=1600 TotalNodes=20 SelectTypeParameters=N/A DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=507904 PartitionName=gpu AllowGroups=ALL AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL AllocNodes=ALL Default=NO DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=UNLIMITED MinNodes=1 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED Nodes=gpu[01-44] Priority=1 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO Shared=NO PreemptMode=OFF State=UP TotalCPUs=880 TotalNodes=44 SelectTypeParameters=N/A DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=57344 PartitionName=phi AllowGroups=ALL AllowAccounts=ALL AllowQos=ALL AllocNodes=ALL Default=NO DefaultTime=NONE DisableRootJobs=NO GraceTime=0 Hidden=NO MaxNodes=UNLIMITED MaxTime=UNLIMITED MinNodes=1 LLN=NO MaxCPUsPerNode=UNLIMITED Nodes=phi[01-18] Priority=1 RootOnly=NO ReqResv=NO Shared=NO PreemptMode=OFF State=UP TotalCPUs=360 TotalNodes=18 SelectTypeParameters=N/A DefMemPerNode=UNLIMITED MaxMemPerNode=57344
:$ scontrol show node node426 NodeName=node426 Arch=x86_64 CoresPerSocket=10 CPUAlloc=0 CPUErr=0 CPUTot=20 CPULoad=0.15 Features=(null) Gres=(null) NodeAddr=node426 NodeHostName=node426 Version=14.11 OS=Linux RealMemory=57344 AllocMem=0 Sockets=2 Boards=1 State=IDLE ThreadsPerCore=1 TmpDisk=0 Weight=1 BootTime=2015-07-27T19:34:56 SlurmdStartTime=2015-07-27T22:15:06 CurrentWatts=0 LowestJoules=0 ConsumedJoules=0 ExtSensorsJoules=n/s ExtSensorsWatts=0 ExtSensorsTemp=n/s
Job Submission¶
In order to create a resource allocation and launch tasks you can submit a batch script.
A batch script, submitted to the scheduling system must specify the job specifications:
- resource queue , default is
compute - number of nodes required
- number of cores per node required
- maximum wall time for the job , (please notice the jobs exceeding wall time will be killed).
To submit a job, user can use the sbatch command.
sbatch my_script
Please check sbatch man for more information.
man sbatch
Define batch script¶
Batch scripts contain
- scheduler directives : lines begin with #SBATCH
- shell commands: UNIX shell (bash) commands
- job steps: created with the
sruncommand
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name=my_script # Job name #SBATCH --ntasks=2 # Number of tasks #SBATCH --time=01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - 1.5 hours module load gnu intelmpi #load any needed modules echo "Start at `date`" cd $HOME/workdir ./a.out echo "End at `date`"
To submit this batch script
sbatch my_script
Job Specifications¶
| Option | Argument | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| --job-name, -J | job_name | Job name is job_name |
| --partition, -p | queue_name | Submits to queue queue_name |
| --account, -A | project_name | Project to charge compute hours |
| --ntasks, -n | number_of_tasks | Total number of tasks |
| --nodes, -N | number_of_nodes | Number of nodes |
| --ntasks-per-node | ntasks_per_node | Tasks per node |
| --cpus-per-task, -c | ntasks_per_node | Threads per task |
| --time, -t | HH:MM:SS | Time limit (hh:mm:ss) |
| --mem | memory_mb | Total memory requirements (MB) |
| --output, -o | stdout_filename | Direct job satndard output to stdout_filename, (%j expands to jobID) |
| --error, -e | stderr_filename | Direct job error to error_file, (%j expands to jobID) |
| --depend, -d | afterok:jobid | Job dependency |
SLURM Environment Variables¶
SLURM provides environment variables for most of the values used in the #SBATCH directives.
| Evironment Variable | Description |
|---|---|
| $SLURM_JOBID | Job id |
| $SLURM_JOB_NAME | Job name |
| $SLURM_SUBMIT_DIR | Submit directory |
| $SLURM_SUBMIT_HOST | Submit host |
| $SLURM_JOB_NODELIST | Node list |
| $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES | Number of nodes |
| $SLURM_CPUS_ON_NODE | Number of cores/node |
| $SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK | Threads per task |
| $SLURM_NTASKS_PER_NODE | Number of tasks per node |
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name=slurm_env #SBATCH --nodes=2 # 2 nodes #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=12 # Number of tasks to be invoked on each node #SBATCH --mem-per-cpu=1024 # Minimum memory required per CPU (in megabytes) #SBATCH --time=00:01:00 # Run time in hh:mm:ss #SBATCH --error=job.%J.out #SBATCH --output=job.%J.out echo "Start at `date`" echo "Running on hosts: $SLURM_NODELIST" echo "Running on $SLURM_NNODES nodes." echo "Running $SLURM_NTASKS_PER_NODE tasks per node" echo "Job id is $SLURM_JOBID" echo "End at `date`"
Job Scripts¶
Here are some sample job submission scripts for different runtime models.
- Serial job: Run serial programs,scripts on a single core.
- MPI job: Run multi-process programs with MPI.
- Hybrid job: Parallel programs with MPI and OpenMP threads.
- GPU job: Utilize GPU accelerators.
- PHI job: Utilize PHI accelrators (offload mode only).
Serial batch script¶
#!/bin/bash #----------------------------------------------------------------- # Serial job , requesting 1 core , 2800 MB of memory per job #----------------------------------------------------------------- #SBATCH --job-name=seraljob# Job name #SBATCH --output=serialjob.%j.out # Stdout (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --error=serialjob.%j.err # Stderr (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --ntasks=1 # Total number of tasks #SBATCH --nodes=1 # Total number of nodes requested #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # Tasks per node #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # Threads per task #SBATCH --mem=2800 # Memory per job in MB #SBATCH -t 01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - (max 48h) #SBATCH --partition=taskp # Submit queue #SBATCH -A testproj # Accounting project # Load any necessary modules module load gnu module load intel # Launch the executable a.out ./a.out ARGS
Pure MPI batch script¶
Launch MPI jobs with srun command
DON’T USE mpirun AND mpiexec
#!/bin/bash #----------------------------------------------------------------- # Pure MPI job , using 80 procs on 4 nodes , # with 20 procs per node and 1 thread per MPI task #----------------------------------------------------------------- #SBATCH --job-name=mpijob # Job name #SBATCH --output=mpijob.%j.out # Stdout (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --error=mpijob.%j.err # Stderr (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --ntasks=80 # Total number of tasks #SBATCH --nodes=4 # Total number of nodes requested #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=20 # Tasks per node #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1 # Threads per task(=1) for pure MPI #SBATCH --mem=56000 # Memory per job in MB #SBATCH -t 01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - (max 48h) #SBATCH --partition=compute # Submit queue #SBATCH -A testproj # Accounting project # Load any necessary modules module load gnu module load intel module load intelmpi export I_MPI_FABRICS=shm:dapl # Launch the executable srun EXE ARGS
Hybrid MPI/OpenMP batch script¶
Launch MPI jobs with srun command
DON’T USE mpirun AND mpiexec
#!/bin/bash #----------------------------------------------------------------- # Hybrid MPI/OpenMP job , using 80 procs on 4 nodes , # with 2 procs per node and 10 threads per MPI task. #----------------------------------------------------------------- #SBATCH --job-name=hybridjob # Job name #SBATCH --output=hybridjob.%j.out # Stdout (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --error=hybridjob.%j.err # Stderr (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --ntasks=8 # Total number of tasks #SBATCH --nodes=4 # Total number of nodes requested #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=2 # Tasks per node #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=10 # Threads per task #SBATCH --mem =56000 # Memory per job in MB #SBATCH -t 01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - (max 48h) #SBATCH --partition=compute # Submit queue #SBATCH -A testproj # Accounting project # Load any necessary modules module load gnu module load intel module load intelmpi export I_MPI_FABRICS=shm:dapl export OMP_NUM_THREADS=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK # Launch the executable srun EXE ARGS
GPU batch script¶
Launch GPU accelerated jobs.
#!/bin/bash #----------------------------------------------------------------- # GPU job , using 80 procs on 4 nodes , # with 2 gpus per node, 1 procs per node and 20 threads per MPI task. #----------------------------------------------------------------- #SBATCH --job-name=gpujob # Job name #SBATCH --output=gpuob.%j.out # Stdout (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --error=gpujob.%j.err # Stderr (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --ntasks=4 # Total number of tasks #SBATCH --gres=gpu:2 # GPUs per node #SBATCH --nodes=4 # Total number of nodes requested #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # Tasks per node #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=20 # Threads per task #SBATCH --mem =56000 # Memory per job in MB #SBATCH -t 01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - (max 48h) #SBATCH --partition=gpu # Run on the GPU nodes queue #SBATCH -A testproj # Accounting project # Load any necessary modules module load gnu module load intel module load intelmpi module load cuda export I_MPI_FABRICS=shm:dapl export OMP_NUM_THREADS=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK # Launch the executable srun EXE ARGS
PHI batch script¶
Launch PHI accelerated jobs.
#!/bin/bash #----------------------------------------------------------------- # PHI job , using 80 procs on 4 nodes , # with 2 phi's per node, 1 procs per node and 20 threads per MPI task. #----------------------------------------------------------------- #SBATCH --job-name=phijob # Job name #SBATCH --output=phijob.%j.out # Stdout (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --error=phijob.%j.err # Stderr (%j expands to jobId) #SBATCH --ntasks=4 # Total number of tasks #SBATCH --nodes=4 # Total number of nodes requested #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # Tasks per node #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=20 # Threads per task #SBATCH --gres:mic:2 # Accelerators per node #SBATCH --mem =56000 # Memory per job in MB #SBATCH -t 01:30:00 # Run time (hh:mm:ss) - (max 48h) #SBATCH --partition=phi # Run on the GPU nodes queue #SBATCH -A testproj # Accounting project # Load any necessary modules module load gnu module load intel module load intelmpi export I_MPI_FABRICS=shm:dapl ## (HOST) OPENMP NUMBER OF THREADS export OMP_NUM_THREADS=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK ## (MIC) OPENMP NUMBER OF THREADS export MIC_ENV_PREFIX=MIC ## (MIC) 60 physical cores 4 hardware threads export MIC_OMP_NUM_THREADS=240 # Launch the executable srun EXE ARGS
Interactive jobs¶
NAN
Job Monitoring¶
Show jobs queue¶
To determine what jobs exist on the system use
:$ squeue --all JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON)
- JOBID: job id
- PARTITION: partition (use
sinfoto list all available partitions) - NAME: partition name
- USER: username
- ST: STate column,
- R: Running
- PD: PenDing
- TO: TimedOut
- S: Suspended
- CD: Completed
- CA: CAncelled
- F: Failed
- NF: Node Failure
To list jobs only for your user, use
squeue -u username
Check job scheduled time to start
squeue --start
squeue -o "%.8i %.9P %.10j %.10u %.8T %.5C %.4D %.6m %.10l %.10M %.10L %.16R"
Please check squeue man for more information.
man squeue
Job information¶
To view detailed job information use
:$ scontrol show job 11841 JobId=11841 JobName=rungmx.sh UserId=ntell(1000) GroupId=ntell(1000) Priority=4294900666 Nice=0 Account=(null) QOS=normal JobState=RUNNING Reason=None Dependency=(null) Requeue=1 Restarts=0 BatchFlag=1 Reboot=0 ExitCode=0:0 RunTime=14:01:51 TimeLimit=2-00:00:00 TimeMin=N/A SubmitTime=2015-07-28T00:51:21 EligibleTime=2015-07-28T00:51:21 StartTime=2015-07-28T00:51:22 EndTime=2015-07-30T00:51:22 PreemptTime=None SuspendTime=None SecsPreSuspend=0 Partition=all AllocNode:Sid=login01:5379 ReqNodeList=(null) ExcNodeList=(null) NodeList=node[001-072] BatchHost=node001 NumNodes=72 NumCPUs=1440 CPUs/Task=1 ReqB:S:C:T=0:0:*:* Socks/Node=* NtasksPerN:B:S:C=20:0:*:* CoreSpec=* MinCPUsNode=20 MinMemoryNode=0 MinTmpDiskNode=0 Features=(null) Gres=(null) Reservation=(null) Shared=0 Contiguous=0 Licenses=(null) Network=(null) Command=/users/staff/ntell/Runs/Oxides/1273/rungmx.sh WorkDir=/users/staff/ntell/Runs/Oxides/1273 StdErr=/users/staff/ntell/Runs/Oxides/1273/slurm-11841.out StdIn=/dev/null StdOut=/users/staff/ntell/Runs/Oxides/1273/slurm-11841.out
Pending Jobs¶
Common reasons for awaiting jobs.
| Dependency | This job is waiting for a dependent job to complete. |
| NodeDown | A node required by the job is down. |
| PartitionDown | The partition (queue) required by this job is in a DOWN state and temporarily accepting no jobs, for instance because of maintenance. Note that this message may be displayed for a time even after the system is back up. |
| Priority | One or more higher priority jobs exist for this partition or advanced reservation. Other jobs in the queue have higher priority than yours. |
| ReqNodeNotAvail | No nodes can be found satisfying your limits, for instance because maintenance is scheduled and the job can not finish before it |
| Reservation | The job is waiting for its advanced reservation to become available. |
| Resources | The job is waiting for resources (nodes) to become available and will run when Slurm finds enough free nodes. |
| SystemFailure | Failure of the SLURM system, a file system, the network, etc |
Job Accounting¶
Accounting information for completed jobs, use the sacct command. (current day)
JobID JobName Partition Account AllocCPUS State ExitCode ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- -------- 17692 Job0 compute testproj 64 CANCELLED+ 0:0 17693 Job1 compute testproj 1 COMPLETED 0:0
You can tailor the output with the use of the --format= option to specify the fields to be shown.
sacct --format=jobid,jobname,partition,user%12,account%12,alloccpus,nnodes,elapsed,cputime,state,exitcode
-e, --helpformat Print a list of fields that can be specified with the --format option. -S, --starttime Select jobs eligible after the specified time. Default is midnight of current day. If states are given with the -s option then return jobs in this state at this time, 'now' is also used as the default time. Valid time formats are... HH:MM[:SS] [AM|PM] MMDD[YY] or MM/DD[/YY] or MM.DD[.YY] MM/DD[/YY]-HH:MM[:SS] YYYY-MM-DD[THH:MM[:SS]]
Accounting information for running jobs, use the sstat command.
Job Cancelling¶
To cancel job, use scancel
scancel job_id
Examples¶
Send SIGTERM to steps 1 and 3 of job 1234:
scancel --signal=TERM 1234.1 1234.3
Cancel job 1234 along with all of its steps:
scancel 1234
Send SIGKILL to all steps of job 1235, but do not cancel the job itself:
scancel --signal=KILL 1235
Cancel all your jobs¶
scancel -u username
Cancel all your pending jobs¶
scancel -t PD
Man page¶
man scancel
Job Dependency¶
Use sbatch --dependency=<dependency_list> option if you need your jobs to run in a specific order.
| DEPENDENCY | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| after | This job can begin execution after the specified jobs have begun execution. |
| afterany | This job can begin execution after the specified jobs have terminated. |
| afternotok | This job can begin execution after the specified jobs have terminated in some failed state (non-zero exit code, node failure, timed out, etc). |
| afterok | This job can begin execution after the specified jobs have successfully executed (ran to completion with an exit code of zero). |
| expand | Resources allocated to this job should be used to expand the specified job. The job to expand must share the same QOS (Quality of Service) and partition. Gang scheduling of resources in the partition is also not supported. |
| singleton | This job can begin execution after any previously launched jobs sharing the same job name and user have terminated. |
Example: “diamond workflow”
Four jobs A,B,C,D. Job A runs first. Jobs B and C depend on completition of job A. Job D depends on jobs B and C.
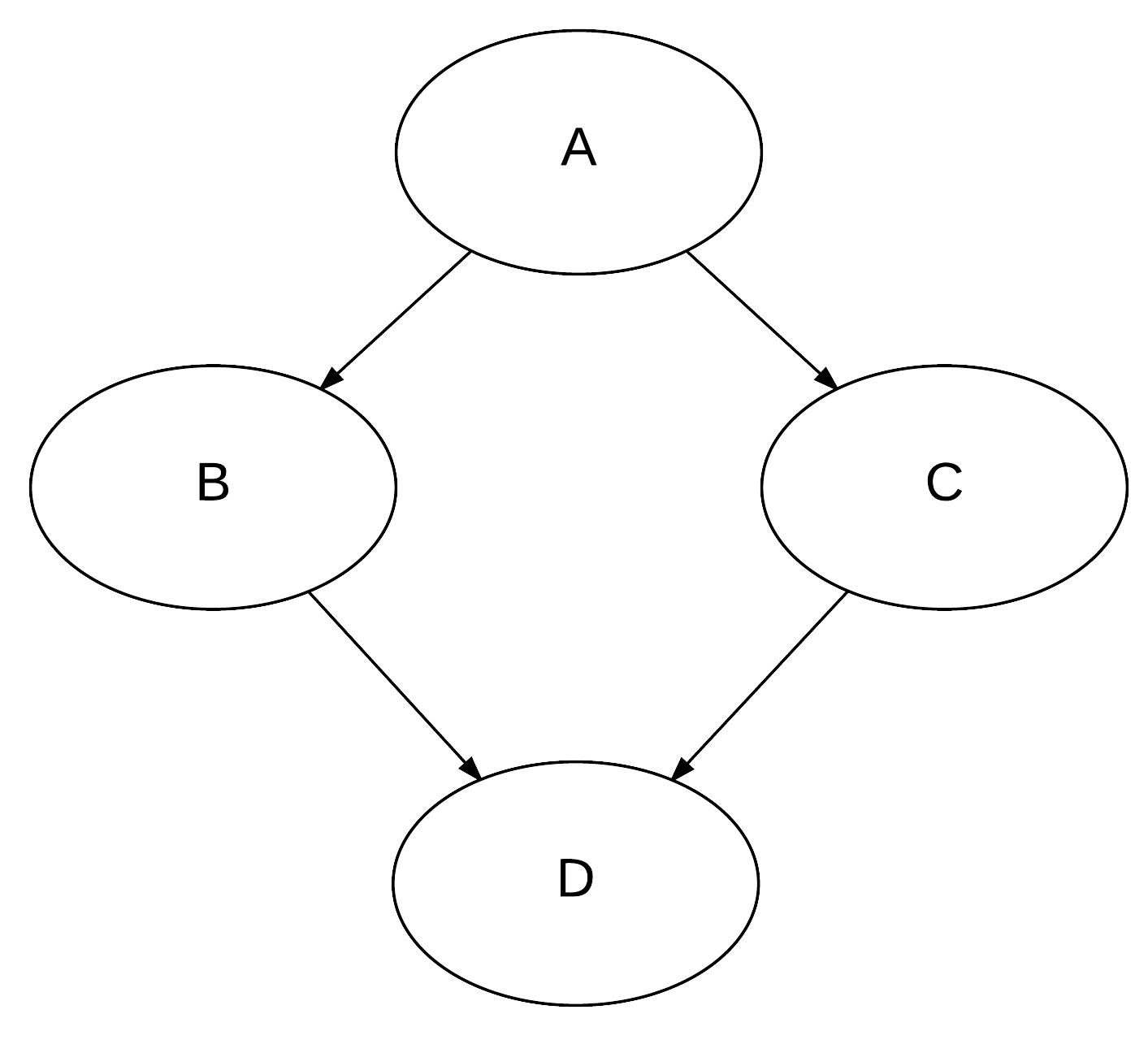
Submit job A first:
$ sbatch A Submitted batch job 17703
Jobs B and C depend on successful completion of job A.
$sbatch -d afterok:17703 B Submitted batch job 17704 $ sbatch -d afterok:17703 C Submitted batch job 17705
Job D depends on successful completion of both jobs B and C
sbatch -d afterok:17704:17705 D Submitted batch job 17706
Check your running queue
$squeue -u <username> JOBID PARTITION NAME USER ST TIME NODES NODELIST(REASON) 17706 compute D nikolout PD 0:00 1 (Dependency) 17704 compute B nikolout R 1:27 1 node260 17705 compute C nikolout R 1:27 1 node260
Job A has already completed so jobs B and C are already running. Job D is on pending state waiting B and C to end.
Chain dependencies¶
Automating dependency steps:
jobA=`sbatch A | awk '{print $4}'` jobB=`sbatch -d afterok:$jobA B | awk '{print $4}'` jobC=`sbatch -d afterok:$jobA C | awk '{print $4}'` jobD=`sbatch -d afterok:$jobB:$jobC D | awk '{print $4}'`
Or, you can submit your dependent jobs from within the job that they depend on.
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH -n 1 #SBATCH -t 00:01:00 #SBATCH -J A sbatch --dependency=afterok:$SLURM_JOB_ID B srun EXE ARGS
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH -n 1 #SBATCH -t 00:01:00 #SBATCH -J B srun EXE ARGS
NOTE Job B will only be considered for scheduling when its dependency has completed.
Usage report¶
mybudget: Check allocated core hours
$ mybudget ======================================================================= Core Hours Allocation Information for account : testproj ======================================================================= Allocated Core Hours : 2400000.00 Consumed Core Hours : 15.00 Percentage of Consumed : 0.00 =======================================================================
myreport: Check consumed core hours and energy.
$ myreport
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cluster/Account/User Utilization 2015-04-07T00:00:00 - 2015-10-07T23:59:59 (15897600 secs)
Time reported in CPU Hours
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Cluster Account Login Proper Name Used Energy
--------- --------------- --------- --------------- ---------- ----------
aris testproj username User Name 15 110
SLURM commands¶
Man pages exist for all SLURM daemons, commands, and API functions. The command option –help also provides a brief summary of options. Note that the command options are all case insensitive.
-
sacctis used to report job or job step accounting information about active or completed jobs. -
sbatchis used to submit a job script for later execution. The script will typically contain one or more srun commands to launch parallel tasks. -
scancelis used to cancel a pending or running job or job step. It can also be used to send an arbitrary signal to all processes associated with a running job or job step. -
scontrolis the administrative tool used to view and/or modify SLURM state. Note that many scontrol commands can only be executed as user root. -
sinforeports the state of partitions and nodes managed by SLURM. It has a wide variety of filtering, sorting, and formatting options. -
squeuereports the state of jobs or job steps. It has a wide variety of filtering, sorting, and formatting options. By default, it reports the running jobs in priority order and then the pending jobs in priority order. -
srunis used to submit a job for execution or initiate job steps in real time. srun has a wide variety of options to specify resource requirements, including: minimum and maximum node count, processor count, specific nodes to use or not use, and specific node characteristics (so much memory, disk space, certain required features, etc.). A job can contain multiple job steps executing sequentially or in parallel on independent or shared nodes within the job’s node allocation.